

For example, you could divide the range 0 - 100 by 5 bins or by 4 bins, making the bin interval either 20 or 25 units. The distribution that is displayed in the visualization is based on how the bins are divided. 0-19, 20 - 39, 40- 59, etc.) with data bucketed into a given range (Ex. The bars in a histogram represent numeric bins (Ex. A common example is a dice roll, by calculating and displaying the predicted frequency distribution of the different numbers that the dice may land on. A probability histogram showcases the data point values that are most likely to occur. This represents the percentage rate chance of any particular data point falling within each range. In statistics, histograms are used to graph the probability distribution of the data. Analysts and statisticians use them to analyze patterns of frequency, and visualize a numerical breakdown of what is being collected in the data. Histograms are useful for analyzing numerical data sets. However, not all histograms need to use a time period as the given range.
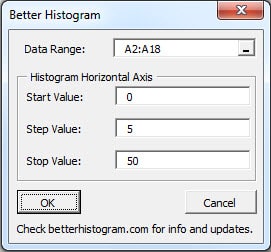
This histogram shows the frequency of visitors to a restaurant in one hour bins within the range of a time frame. You’ve probably seen a histogram searching for the best time to visit a restaurant on Google! Histograms are graphs and are one way to visualize frequency distributions. A frequency distribution is the display of how often something occurred in a graph, table, or diagram. These bars are called bins or buckets, and together they represent what is called a frequency distribution. While histograms look like bar charts, they are different in that each bar is an interval of values of a metric.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
